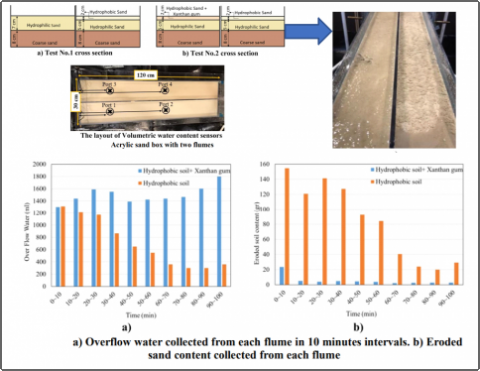
The goal of this project is to establish new procedures for temporary protection of wildfire affected slopes against mudslides and surface erosion. Biopolymers are proposed to be used due to low environmental impact, low cost, wide availability, and relatively short time needed for safe biodegradation. While other currently used similar slope covering agents, such as are mulches or synthetic polymers, may be a long-term solution, such approaches are invalid because they introduce new species and chemicals in soil. There is a strong need to not impact local biodiversity and thus to find a solution for temporary protection. There is a critical need to protect natural soil from eroding while permitting soil particles to recover from hydrophobicity. The best solution are temporary coverings of vulnerable slopes with biopolymers which will protect soil particles from removal by rain impact and allow the hydrophobicity to naturally reverse within a period of one to two years. Since application with agricultural drones is quite easy and versatile and biopolymers are cheap, it is possible to quickly re-apply the cover if necessary. The specific objectives are to: (1) correlate soil type, slope angle, hydrophobicity level and rain intensity to rate of water runoff and sediment erosion; (2) assess a short-term effectiveness of full and patterned partial slope coverage with biopolymer; (3) propose optimal procedure for drone-assisted slope coverage with biopolymer and (4) evaluate long-term environmental impacts on water runoff and erosion in test slopes.
Project duration
-
Project description